今天推介一个新的BCL北京城市实验室项目“城市绿色基础设施”
该项目涵盖《解读城市公园的休闲用途:针对中国所有城市的多源大数据实验》、《基于多源新数据的城市绿地多尺度评价:中国主要城市探索》等研究内容,此外设有【《风景园林》大数据与城市绿色基础设施专辑】,收录了大数据与城市绿色基础设施这一方向的七篇论文,涵盖了设施使用评价与设施规划设计支持两方面内容,所使用的数据涵盖了遥感大数据、咕咚App大数据、摩拜单车大数据、兴趣点大数据以及百度街景大数据等,以供大家学习与交流。
此外,这一方面的多个项目的研究工作正在继续,考虑到内容没有发表,后续时机成熟时继续补充推送。


《解读城市公园的休闲用途:针对中国所有城市的多源大数据实验》
Deciphering the recreational use of urban parks: Experiments using multi-source big data for all Chinese cities
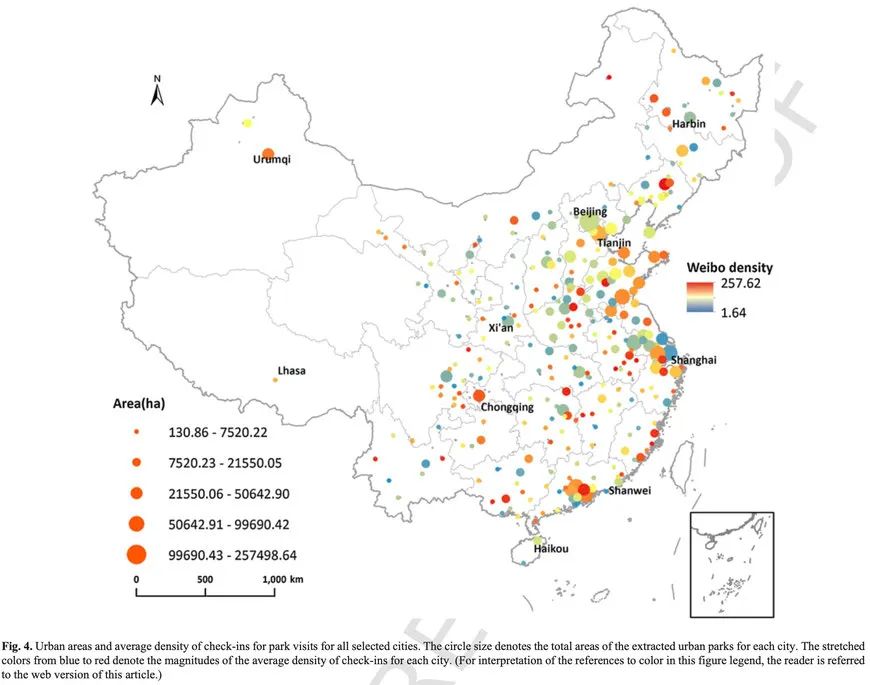
Chinas rapid urbanization process has accentuated the disparity between the demand for and supply of its park recreational services. Estimations of park use and an understanding of the factors that influence it are critical for increasing these services. However, the data traditionally used to quantify park use are often sub- jective as well as costly and laborious to procure. This paper assessed the use of parks through an analysis of check-in data obtained from the Weibo social media platform for 13,759 parks located in all 287 cities at prefecture level and above across China. We investigated how park attributes, accessibility, and the socioe- conomic environment affected the number and density of park check-ins. We used multiple linear regression models to analyze the factors influencing check-ins for park visits. The results showed that in all the cities, the influence of external factors on the number and density of check-in visits, notably the densities of points of interest (POIs) and bus stops around the parks was significantly positive, with the density of POIs being the most influential factor. Conversely, park attributes, which included the park service area and the landscape shape index (LSI), negatively influenced park use. The density of POIs and bus stops located around the park positively influenced the density of the recreational use of urban parks in cities within all administrative tiers, whereas the impact of park service areas was negative in all of them. Finally, the factors with the greatest influence varied according to the administrative tiers of the cities. These findings provide valuable inputs for increasing the efficiency of park use and improving recreational services according to the characteristics of different cities.
PS:以下为【北京城市实验室 Urban Green Infrastructure 单元】分享内容目录,具体内容可进入网站下载查看。

《基于多源新数据的城市绿地多尺度评价:中国主要城市探索》
Muiti-scale Evaluation of Urban Green Space Based on Muti-source New Data: Exploration of Main Cities in China
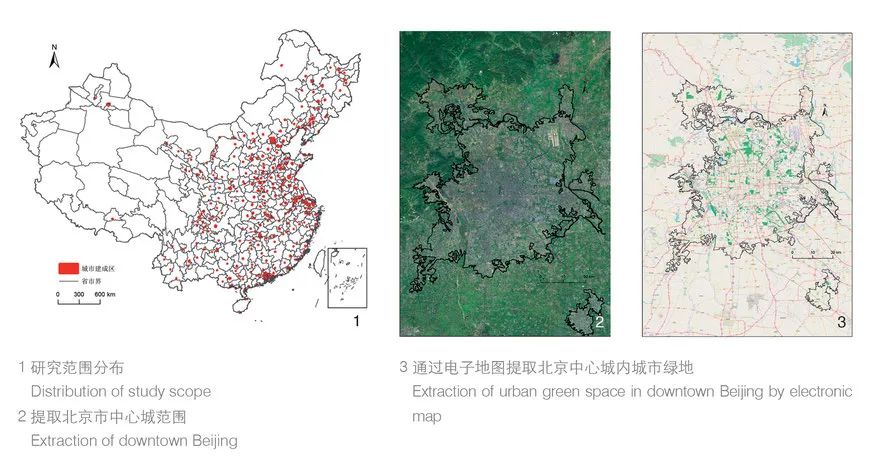
The scientific evaluation of urban green space provides data support for green space planning, and it plays an important role in building sustainable and healthy city. This paper develops an indicator system for evaluating the urban green space under the new data environment, from the perspectives such as shape, quality, vitality, and service level. Then based on the theory of “Big Model”, the paper carries out multi-scale assessments of the green space in central area of 287 Chinese cities, and take Zunyi as a case study of evaluating the quality and vitality of urban green space. To make the research more objectivity, unity, and comparability, we solved several key issues including the extraction of spatial data of urban green space, and the definition of central city. The results show that: At the scale of green patch, the overall compactness of urban green space is high, and most green spaces are located near the city center. At the urban scale, the average service level of urban green space of 287 Chinese cities is 57.45%, while the sub-provincial cities have the highest average service level, and the prefecture-level cities have the lowest service level. This paper analyzes the shortages and problems of the national urban green space in the country in order to provide reference for the construction of urban green space in the future.
PS:以下为【北京城市实验室 Urban Green Infrastructure 单元】分享内容目录,具体内容可进入网站下载查看。

《风景园林》大数据与城市绿色基础设施专辑】
The Special Issue published in Landscape and Architecture

城市绿色基础设施作为城市公共空间的重要组成部分,对城市居民的日常生活具有重要影响,是其城市生活中不可或缺的一部分。城市绿色基础设施,近年来得到了政府的极大重视和支持,如登山步道、城市绿道、中央公园、街头微型公园、街道绿化等。如何科学合理地对这类基础设施进行科学布局与类型选择,如何对已建设基础设施的使用情况和实施效果进行客观评价,都是学界业界特别关注的主题。
近年来出现的大数据,提供了从更微观、更全面、更多维度、更实时地认识城市空间以及城市活动的机会。利用大数据来研究城市绿色基础设施具有较大潜力,使我们有机会客观认识绿色基础设施及其所承载的城市活动,不仅可以对设施的使用情况进行评价,还可以对设施的规划设计提供技术支持。这是对城市绿色基础设施这一领域以往偏经验偏质性研究的必要补充。
本期收录了大数据与城市绿色基础设施这一方向的论文共七篇,涵盖了设施使用评价与设施规划设计支持两方面内容,所使用的数据涵盖了遥感大数据、咕咚App大数据、摩拜单车大数据、兴趣点大数据以及百度街景大数据等。
——专题主持人:龙瀛,清华大学建筑学院,特别研究员/博士生导师
PS:以下为【北京城市实验室 Urban Green Infrastructure 单元】分享内容目录,具体内容可进入网站下载查看。
欢迎大家点击文末的“阅读原文”或复制搜索此链接:https://www.beijingcitylab.com/projects-1/35-urban-green-infrastructure/,关注北京城市实验室 Urban Green Infrastructure 单元深入探索。
更多内容,请点击微信下方菜单即可查询。
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。
Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:孟庆祥
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):项目推送|城市绿色基础设施 Urban Green Infrastructure
 规划问道
规划问道



