本期为大家推荐的内容为论文《Measuring pedestrian flows in public spaces: Inferring walking for transport and recreation using Wi-Fi probes》(测度公共空间的行人流量:使用Wi-Fi探针推测交通与休闲步行),发表在Building and Environment期刊,欢迎大家学习与交流。
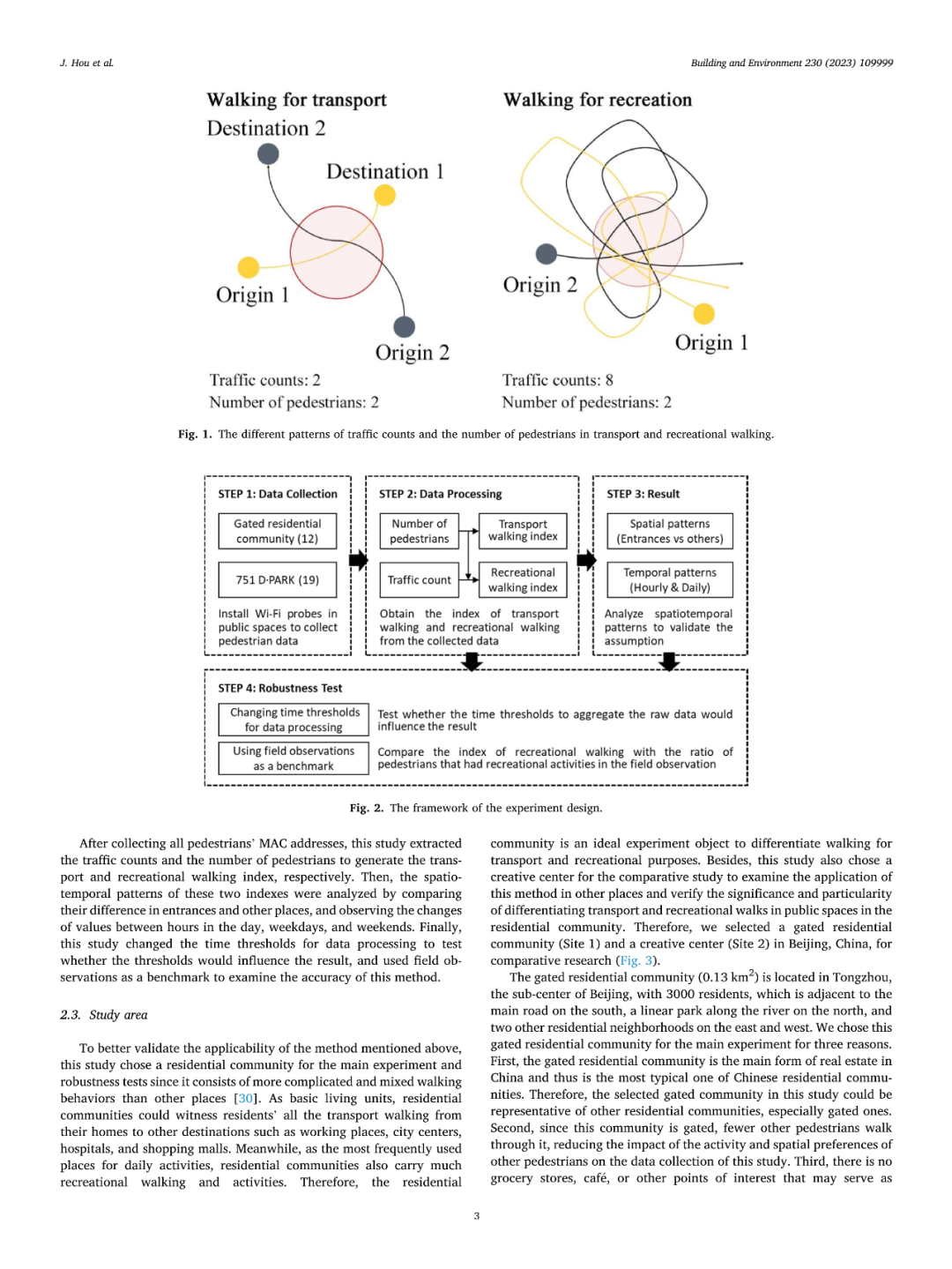
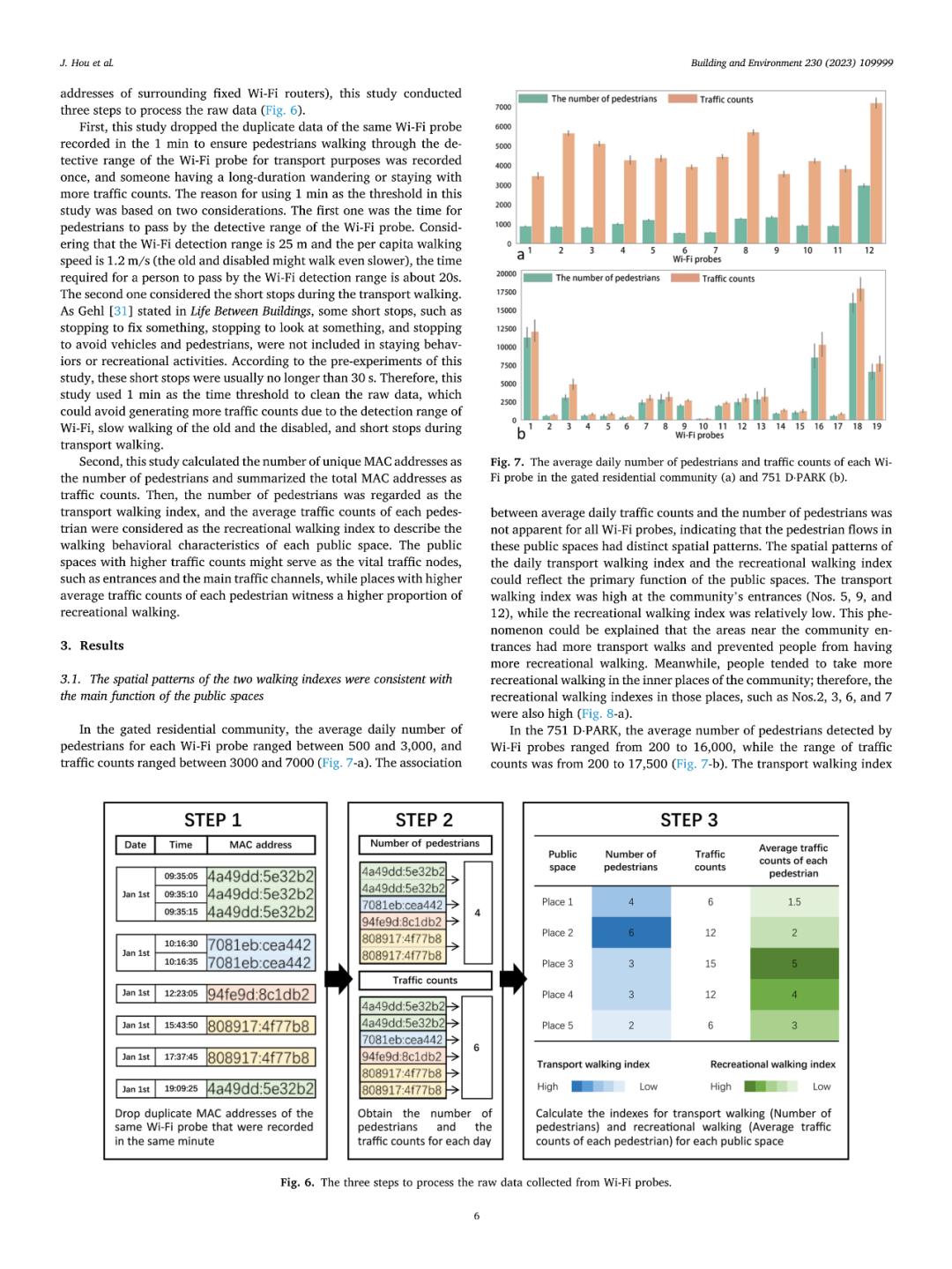
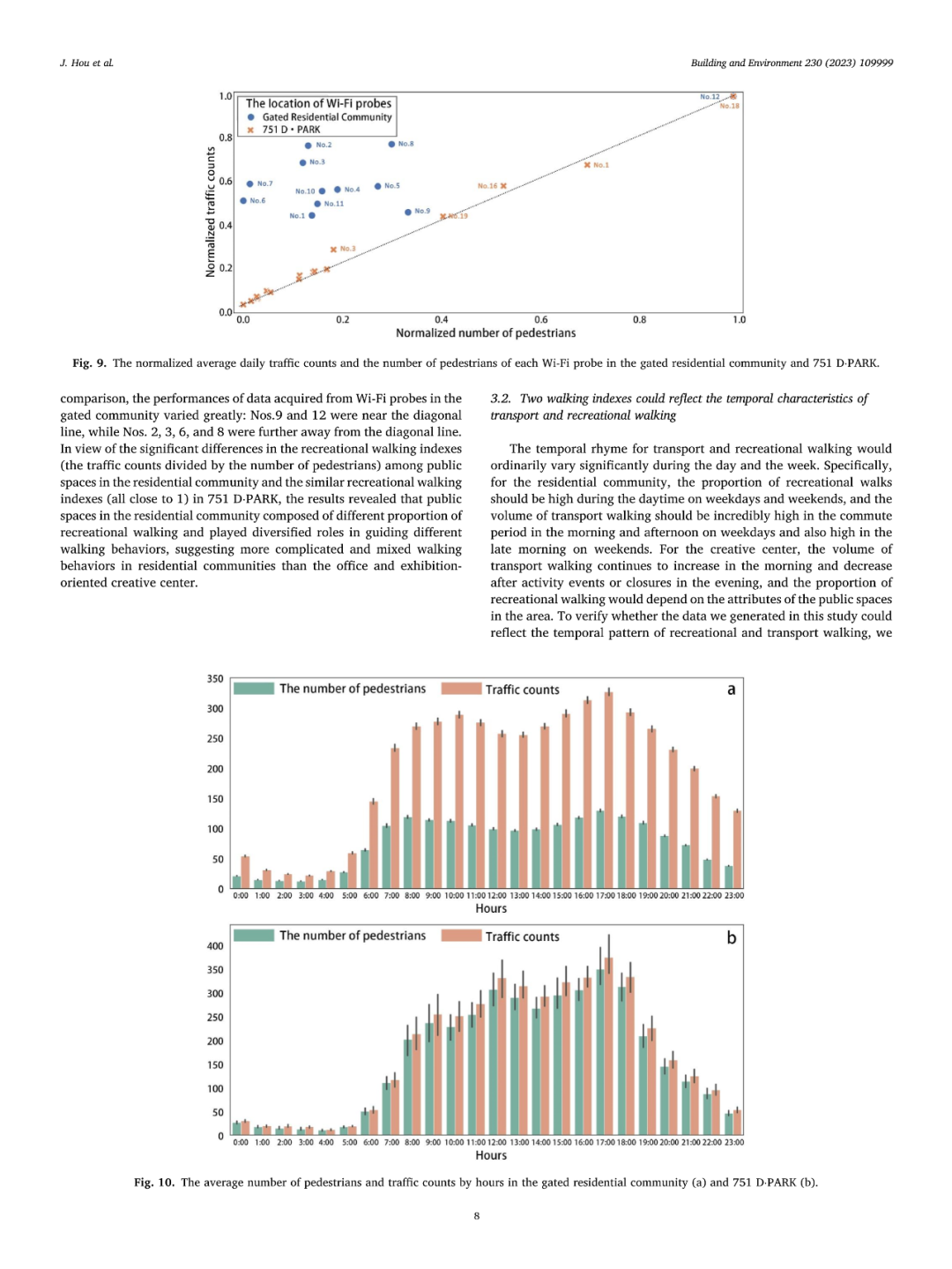
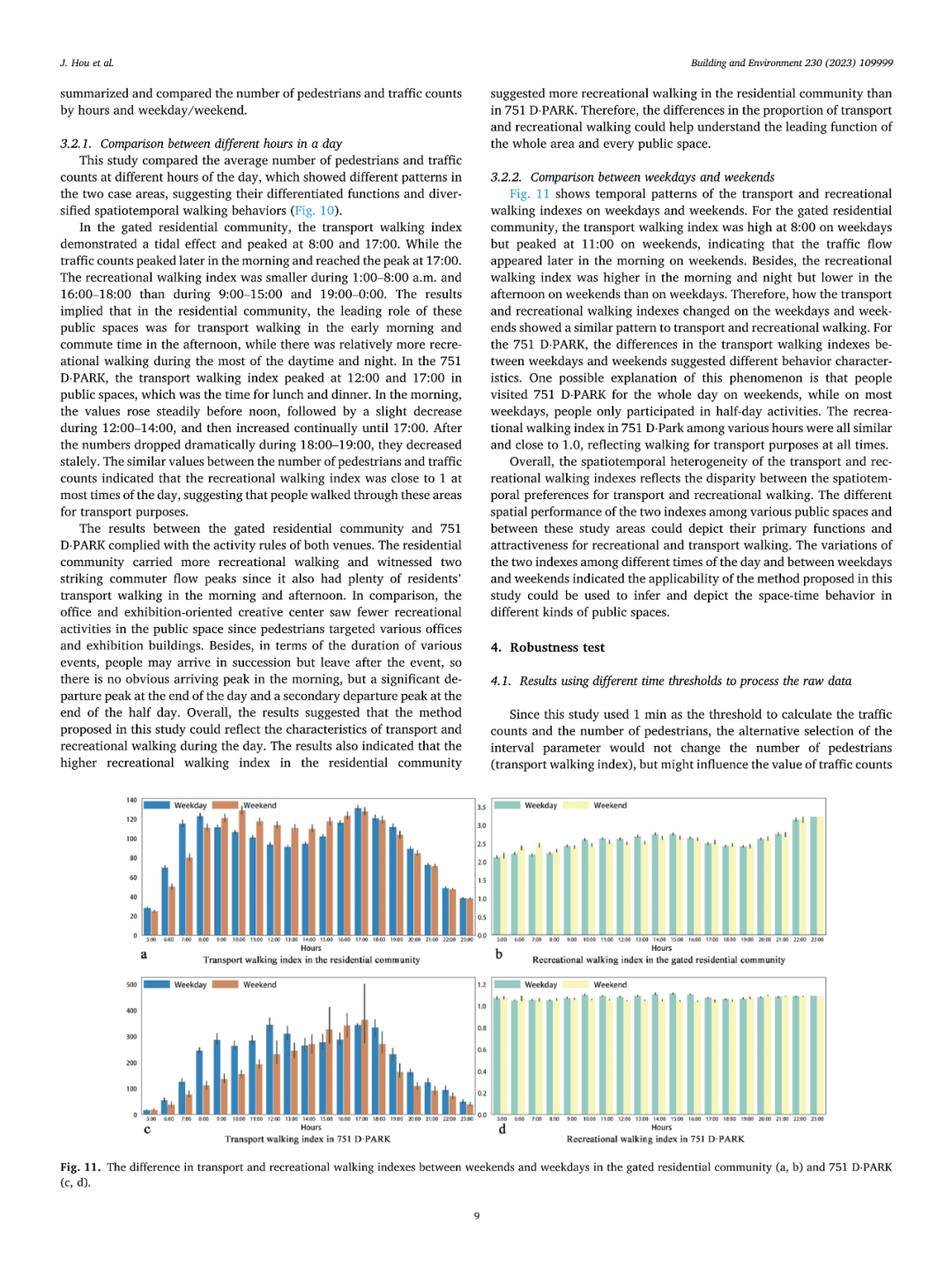
区分公共空间的交通和休闲步行行为可以促进公共空间的精细化设计以满足不同的步行需求、鼓励更多的步行行为。然而,以往的研究主要依赖于个体层面的实地观察和自我报告,未能从空间层面定量区分和描述特定空间内行人的交通和休闲步行的整体情况。本研究提出了一种基于人数及人次数据推测公共空间中交通和休闲步行情况的定量测度方法。研究在北京一处门禁小区和751创意中心展开了使用Wi-Fi探针收集行人数据的对比实验,以验证该方法的适用性。研究结果表明,交通步行指数(人数数据)可以刻画交通步行流量,而休闲步行指数(人均人次数据)可以反映公共空间中休闲步行的比例。研究还通过改变处理数据的时间阈值参数和现场观察的分析结果对比验证了结果的稳健性。鉴于该方法可以实现对公共空间中步行行为的低成本和长时间观察,其可以支持更多公共空间的使用后评估和环境行为学研究,以促进公共空间的可步行性。


题目:Measuring pedestrian flows in public spaces: Inferring walking for transport and recreation using Wi-Fi probes
(测度公共空间的行人流量:使用Wi-Fi探针推测交通与休闲步行)
作者:Jingxuan Hou, Enjia Zhang, Ying Long
发表刊物:
Building and Environment
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.109999
摘要ABSTRACT
With rapid urbanization, the urban environment, especially the neighborhood environment, has received increasing global attention. However, a comprehensive overview of the association between neighborhood risk factors and human health remains unclear due to the large number of neighborhood risk factor–human health outcome pairs.Differentiating transport and recreational walking in public spaces could promote the precise design of walkable public spaces for different walking demands to encourage more walking behaviors. However, previous studies mainly relied on field observations and self-reports, failing to quantitatively distinguish and depict the spatial level usage of transport and recreational walking of all pedestrians passing by. This study proposed an approach based on the traffic counts and the number of pedestrians to infer transport and recreation walking in public spaces. A comparative experiment using Wi-Fi probes to collect pedestrian data in a gated residential community and a creative center in Beijing, China, was conducted to verify the applicability of this method. The results demonstrated that the transport walking index (the number of pedestrians) could portray the volume of transport walking, and the recreational walking index (average traffic counts of each pedestrian) could depict the proportion of recreational walking in public spaces. Two tests using different time threshold parameters and field observations verified the robustness of the results. Given the low-cost and long-duration observation, this method can potentially support the process of Post Occupancy Evaluation and Environment and Behavior research in more public spaces to make them more walkable.






更多相关的研究工作详见BCL的【Sensing Public Space】单元链接:
https://www.beijingcitylab.com/projects-1/55-sensing-public-space/
(复制至浏览器搜索或点击文末“阅读原文”查看)
BCL北京城市实验室“公共空间感知” (Sensing Public Space)项目涵盖《基于视频数据的人群轨迹对小型公共空间活力分析与评价使用的建模》、《使用深度卷积神经网络量化小型公共空间的使用》、《基于空间轨迹熵的公共空间活力表征》等研究内容,欢迎探索。
更多内容,请点击微信下方菜单即可查询。
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。

Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:侯静轩、张恩嘉、张业成
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):论文推荐 | 测度公共空间的行人流量:使用Wi-Fi探针推测交通与休闲步行
 规划问道
规划问道









