本期为大家推荐的内容为论文《CGNet-PIE: A causal generative approach for urban planning intervention effect estimation》(CGNet-PIE:一种用于城市规划干预效果评估的因果生成方法),发表在Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology期刊,欢迎大家学习与交流。
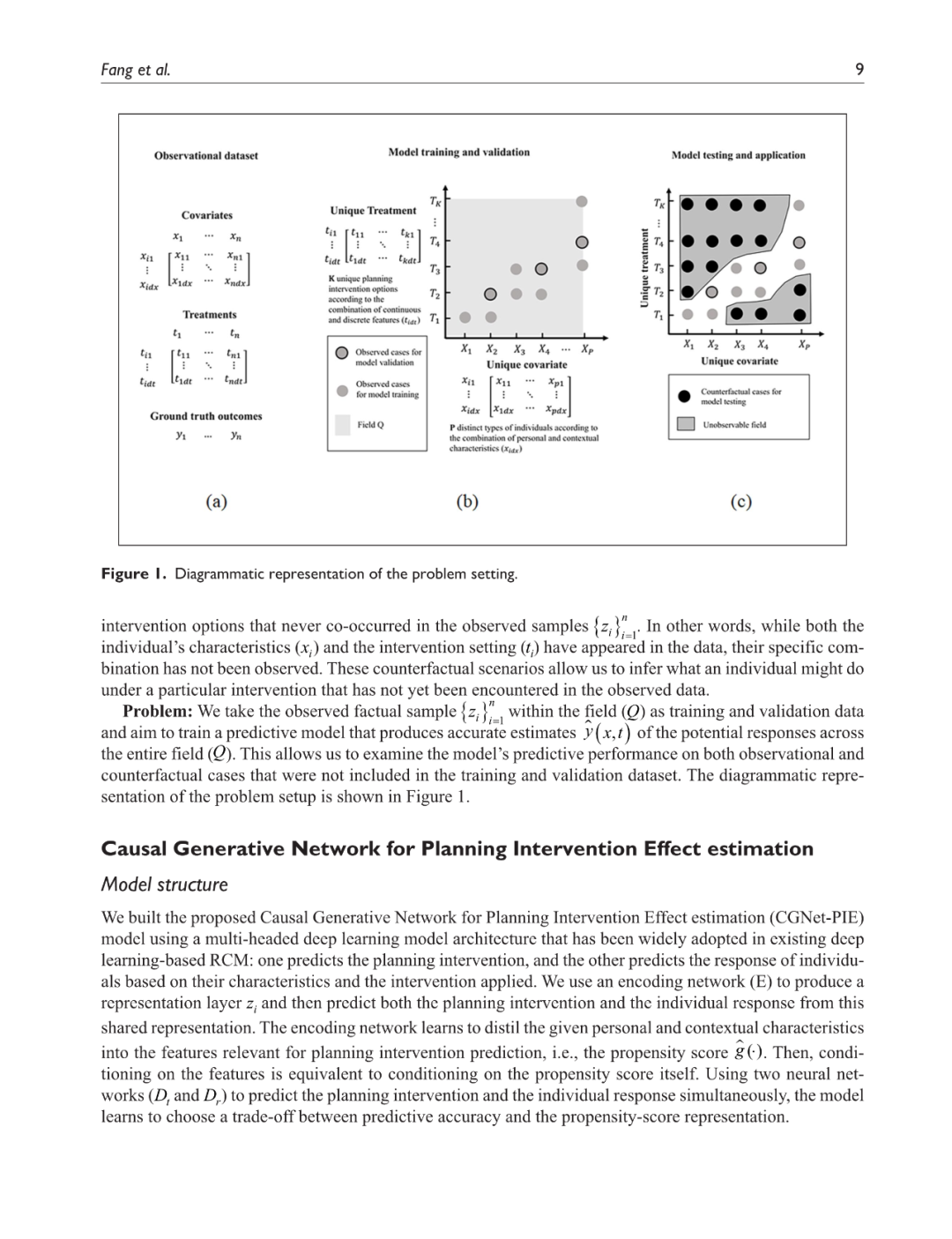
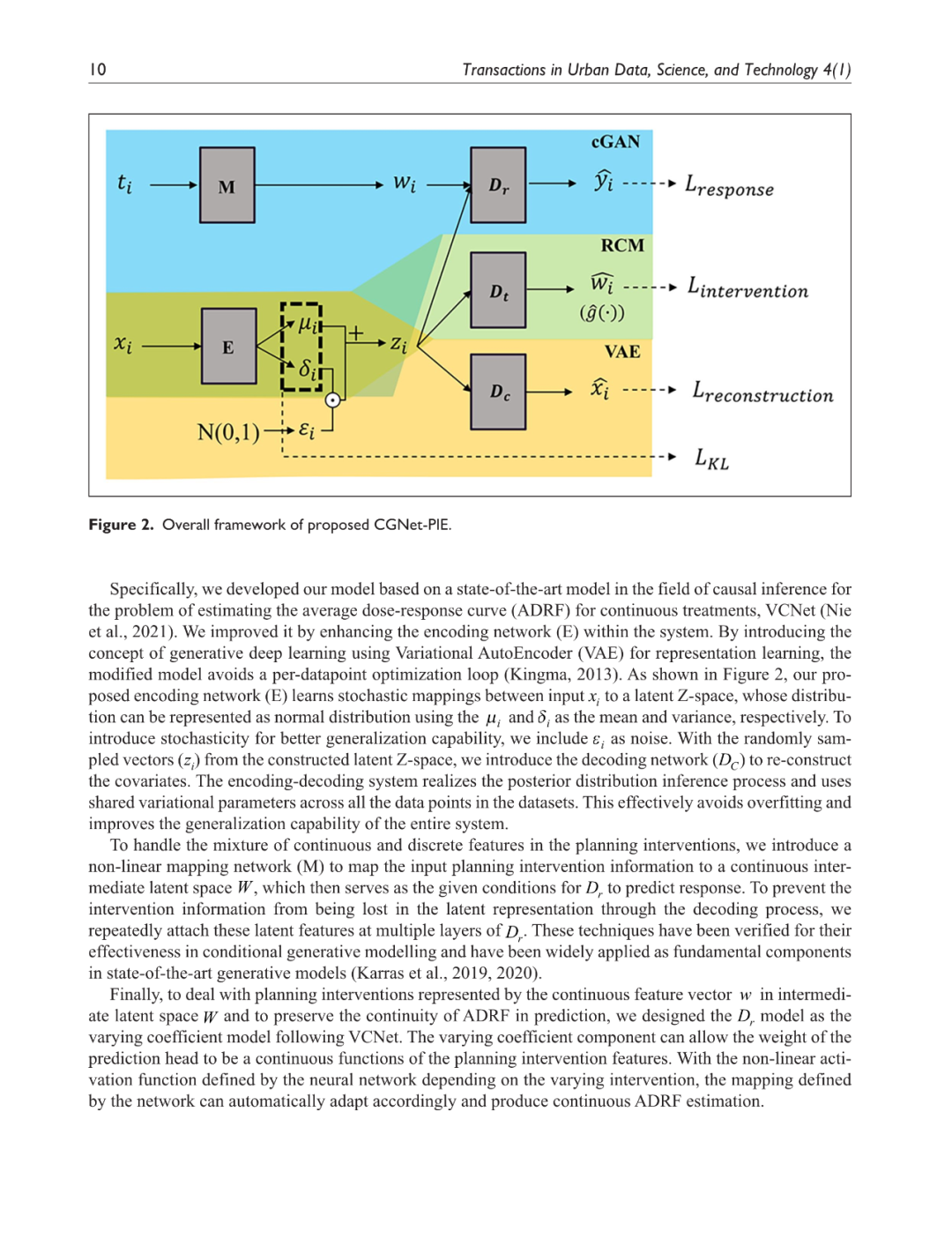
城市规划师面临的核心挑战之一是在规划干预实施之前准确评估其潜在影响。然而,当前的城市规划干预效果评估方法存在显著局限性。关联建模方法虽然能够有效捕捉干预措施与观测结果之间的复杂关系,但无法直接估计因果效应,因此在反事实预测方面存在较大不确定性。操作建模方法通常依赖结构性因果模型,通过对简化因果关系的主观假设,将规划干预转化为预期结果。尽管这些方法能够清晰表达因果机制,但其对城市及人类行为的动态性和复杂性的刻画能力相对受限。本研究提出了一种用于规划干预效果评估的因果生成网络(Causal Generative Network for Planning Intervention Effect estimation, CGNet-PIE),该方法轻量化但具备较高的稳健性,能够直接从观测数据中估计因果效应,而无需完整构建因果交互模型。CGNet-PIE 通过结合生成式深度学习与Rubin 因果模型,有效捕捉非线性关系,提升因果推断能力,从而实现可靠且具备泛化能力的反事实预测。基于合成数据、半合成数据和真实世界数据的实验表明,CGNet-PIE 在准确性和泛化能力方面优于基线模型。该方法为城市规划提供了一种强有力的工具,能够辅助规划师优化决策,实现更加科学的政策制定和资源配置。
题目:CGNet-PIE: A causal generative approach for urban planning intervention effect estimation
(CGNet-PIE:一种用于城市规划干预效果评估的因果生成方法)
作者:
Zhou Fang*, Qianmu Zheng, Shuwen Zheng, Liang Zhao*
发表刊物:
Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology
URL:
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/27541231251318348
引用格式:
Fang, Z., Zheng, Q., Zheng, S., & Zhao, L. (2025). CGNet-PIE: A causal generative approach for urban planning intervention effect estimation. Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology, 27541231251318348.
A critical challenge for urban planners lies in estimating the potential impacts of planning interventions before their implementation. Current approaches to urban planning intervention effect estimation encounter notable constraints. Association modelling approaches, while effective at capturing complex relationships between interventions and outcomes in observed cases, fail to estimate causal effects, making them unreliable for counterfactual predictions. Operational modelling approaches frequently set up structural causal models to transform interventions into outcomes based on subjective assumptions about simplified causal relationships. These approaches, while achieving a clear representation of causality, compromise the ability to accurately model the dynamic and intricate nature of cities and human behaviour. This paper introduces the Causal Generative Network for Planning Intervention Effect estimation (CGNet-PIE), a lightweight yet robust approach that directly estimates causal effects from observed data without the need for fully articulated causal interaction models. By integrating generative deep learning with the Rubin Causal Model, CGNet-PIE effectively captures non-linear relationships and enhances causal inference for reliable and generalizable counterfactual predictions. Experiments on synthetic, semi-synthetic, and real-world datasets demonstrate CGNet-PIE’s superior accuracy and generalization compared to baseline models. CGNet-PIE offers a powerful tool for planners to improve decision-making for informed policymaking and optimal resource allocation.
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。
Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:张业成
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):论文推荐 | CGNet-PIE:一种用于城市规划干预效果评估的因果生成方法








 规划问道
规划问道









