本期为大家推荐的内容为论文《Decoding the association between urban streetscape skeletons and urban activities: Experiments in Beijing using Dazhong Dianping data》(解码城市街道景观骨架与城市活动之间的关联:利用大众点评数据在北京进行的实验),发表在Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology期刊,欢迎大家学习与交流。
城市街道景观骨架在建设充满活力的街道中的重要作用已被反复强调。然而,大多数研究集中于宏观尺度或中观尺度的城市形态或使用定量方法测量街道景观骨架,未能系统地考察街道尺度的城市形态与城市活动之间的关系。本研究以街道段为分析单元,通过控制其他建成环境要素,分析大众点评网上评论密度所代表的城市活动与街道景观骨架的关系。使用多元线性回归、空间滞后模型和随机森林回归等模型,结果表明,在开展活动时,人们更喜欢街道的优点,但忽略了它的缺点。研究结果显示了一些与城市活动相关的指标,如街道的宽度、围合度以及街道两侧更高、更连续的建筑。此外,研究结果还表明,一些街道景观骨架,如宽高比和长度,在离街道中心线不同距离的在线评论中有不同的表现。这些发现可以帮助城市设计师重新思考城市活动和街道层面的城市形态之间的相互作用。


题目:Decoding the association between urban streetscape skeletons and urban activities: Experiments in Beijing using Dazhong Dianping data
(解码城市街道景观骨架与城市活动之间的关联:利用大众点评数据在北京进行的实验)
作者:Enjia Zhang, Hanting Xie & Ying Long
发表刊物:
Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1177/27541231221143608
摘要ABSTRACT
The essential role of urban streetscape skeletons in fostering vibrant streets has been repeatedly emphasized. However, most research focused on the macro-scale or mesoscale urban form or measuring streetscape skeletons using quantitative methods, failing to systematically examine the relationship between the street-level urban form with urban activities. This study took street segments as the analytic unit to analyze the relationship between streetscape skeletons and urban activities represented by the density of online reviews on the Dazhong Dianping by controlling other built environments. Using models like Multiple Linear Regression, Spatial Lag Model, and Random Forest Regression, the result suggested that when conducting activities, people preferred the strengths of the street but ignored its weaknesses. The findings demonstrated some skeleton indicators associated with urban activities, such as the width and enclosure of the street and the higher and more continuous buildings on the side of the streets. Moreover, the result also suggested that some streetscape skeletons, such as cross-section and length, have differentiated performances for online reviews at different distances to the street centerlines. These findings could help urban designers to rethink the interaction between urban activities and street-level urban form.



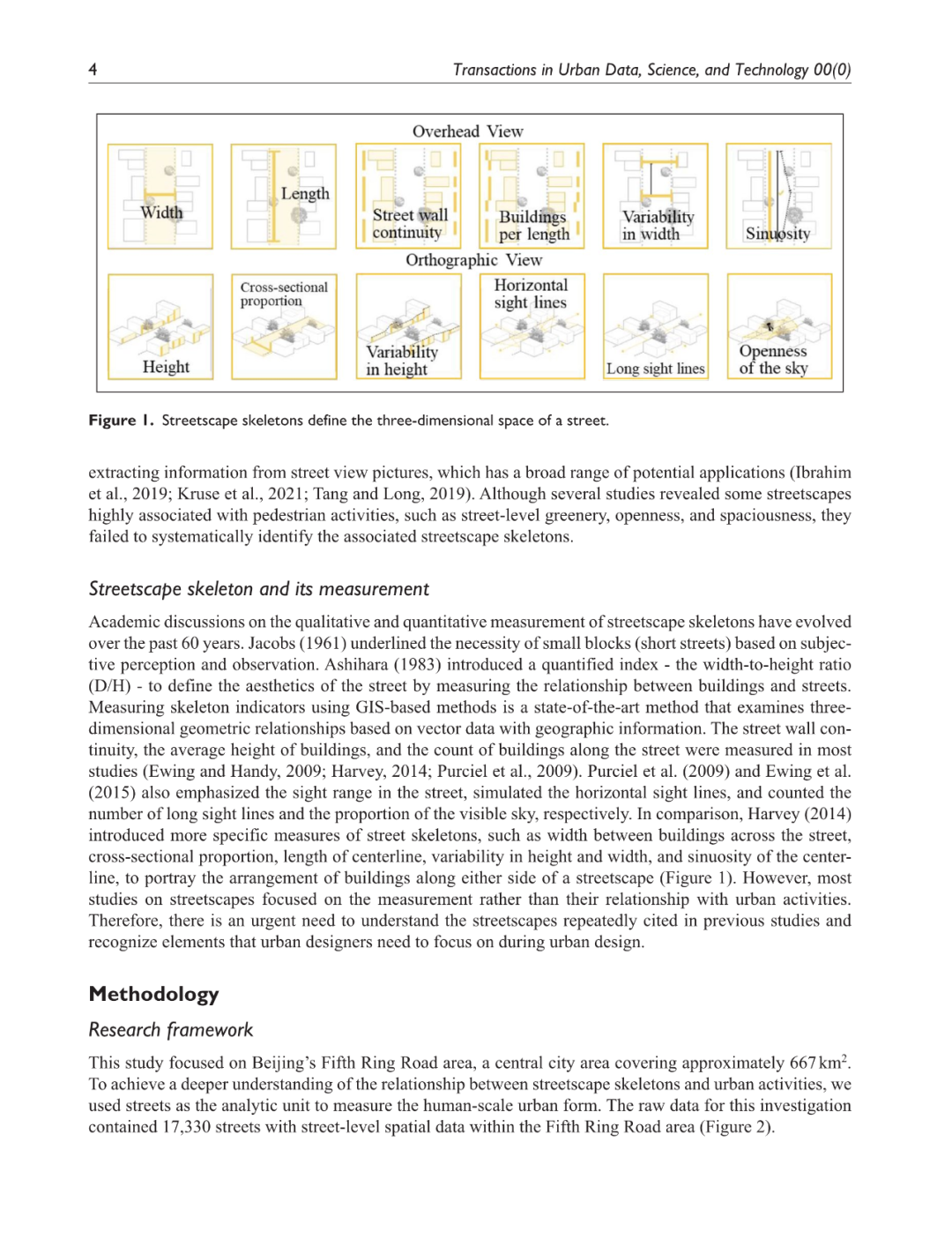

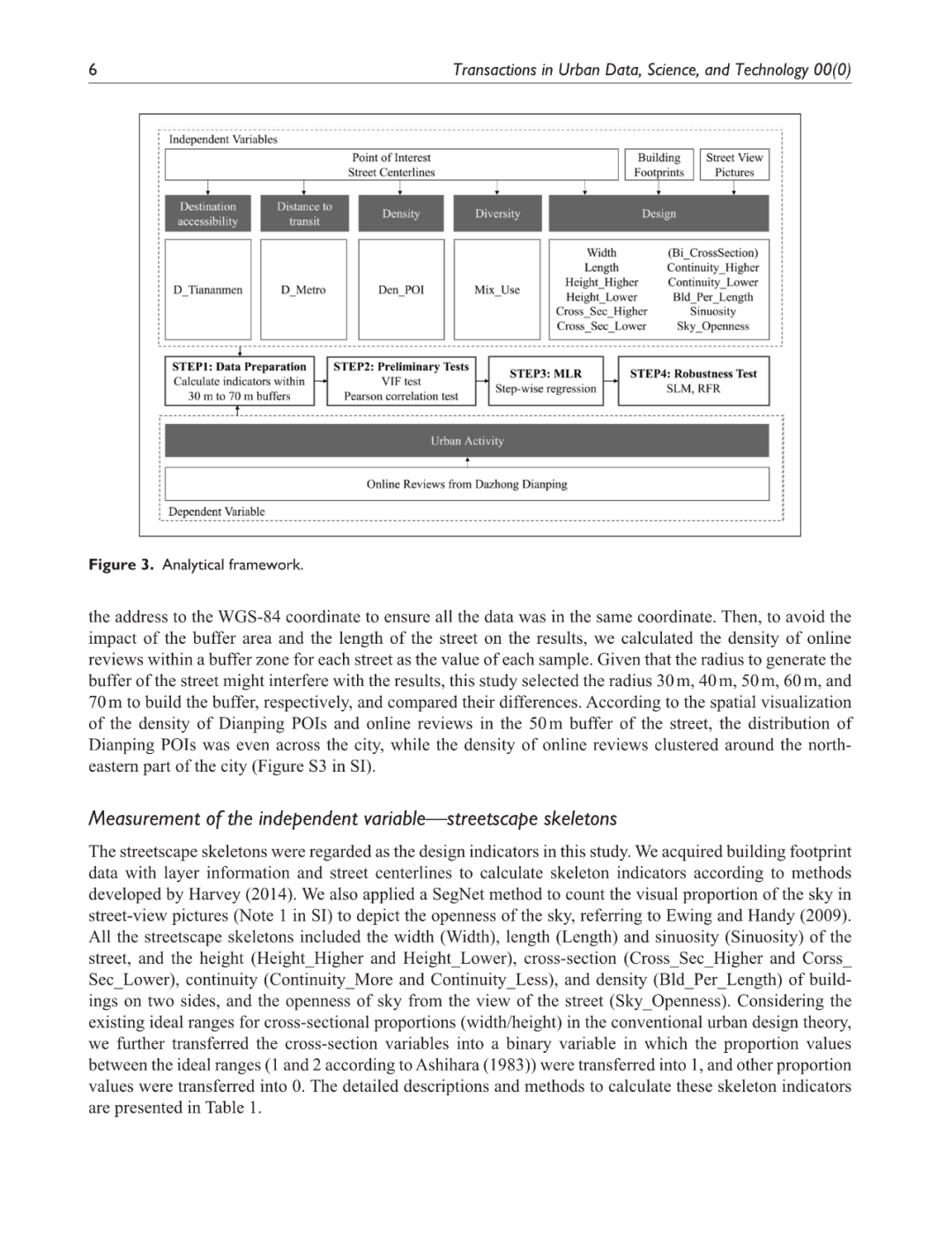
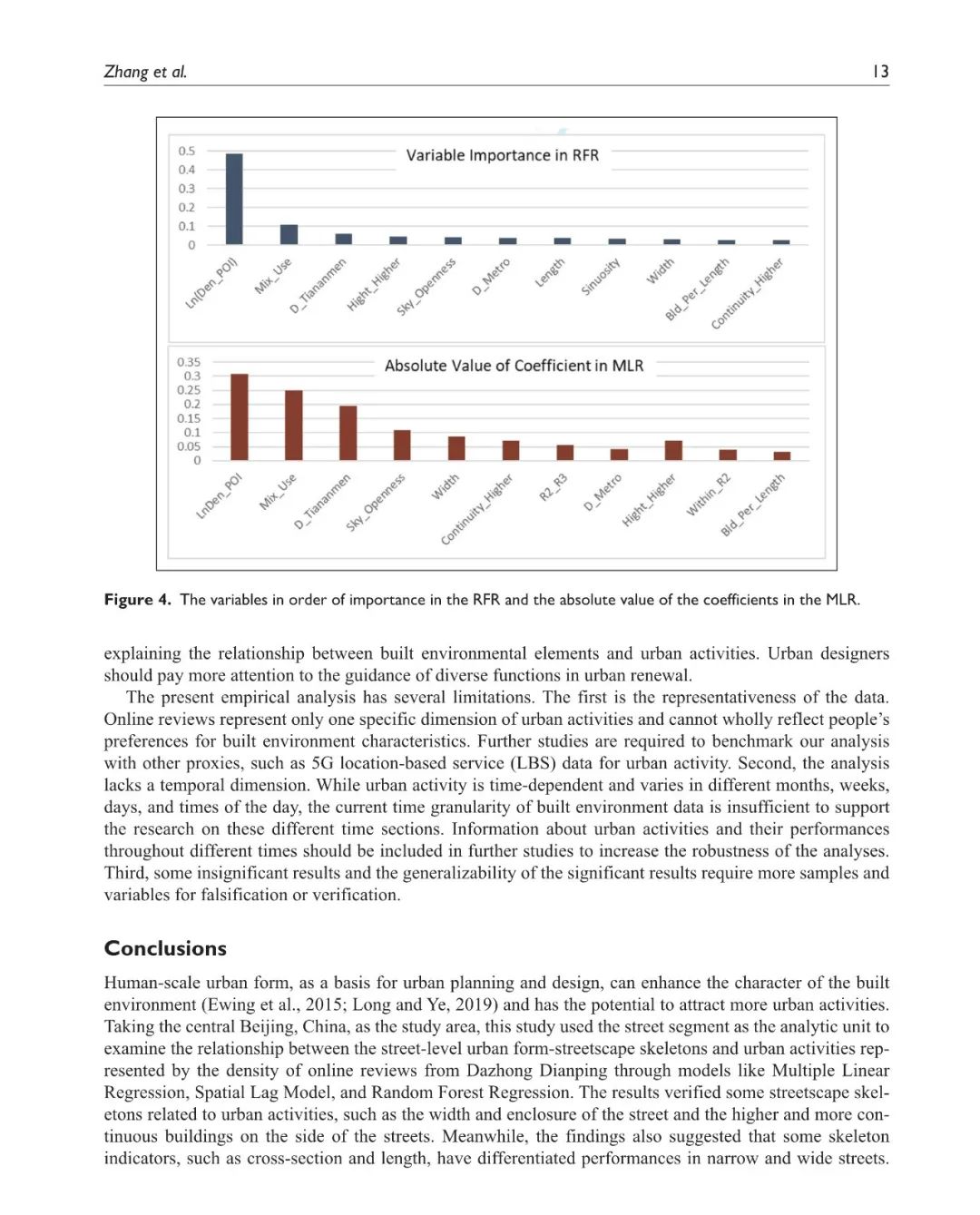


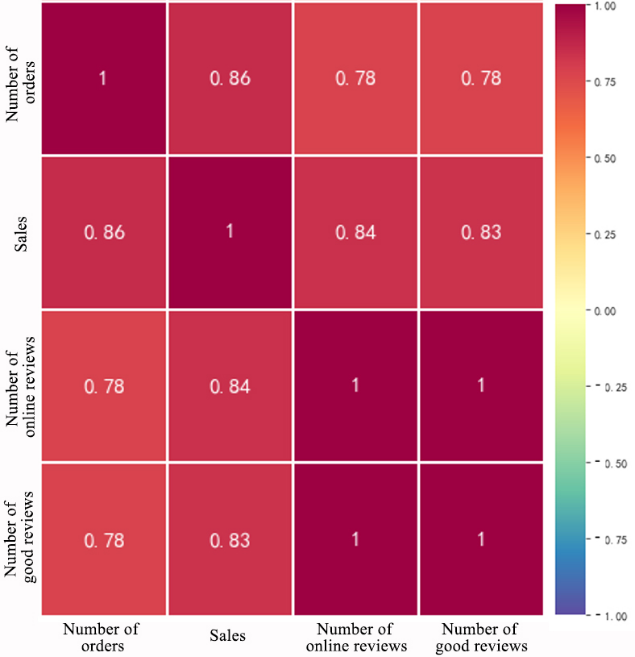
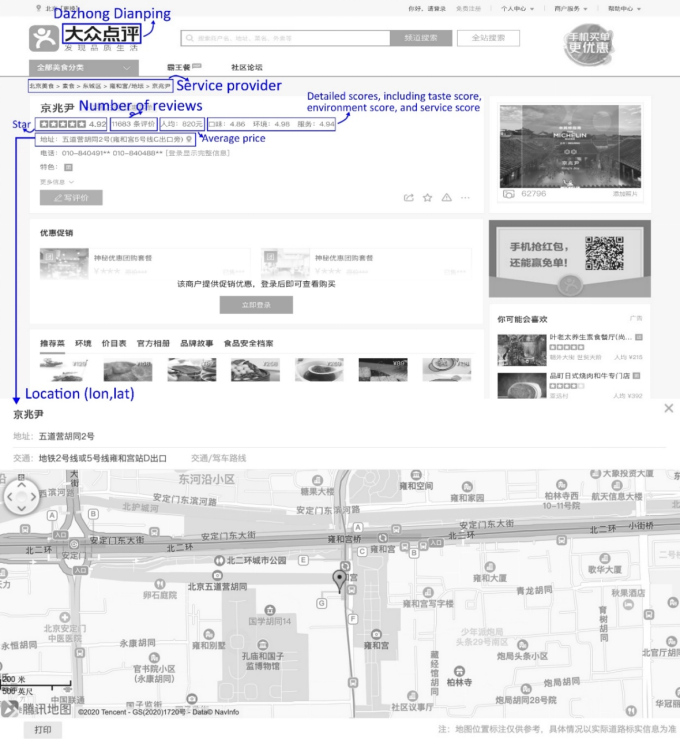
Figure S2. A detailed page of Dazhong Dianping and attributes used in this research.
研究全文、数据以及更多相关的研究工作详见BCL的【Urban Vitality and Urban Design】单元链接:
https://www.beijingcitylab.com/projects-1/26-urban-vitality-and-urban-design/
(复制至浏览器搜索或点击文末“阅读原文”查看)
BCL北京城市实验室“城市活力与城市设计” (Urban Vitality and Urban Design)项目还包括《街区大小重要吗?城市设计对中国城市经济活力的影响》等研究内容,欢迎探索。
更多内容,请点击微信下方菜单即可查询。
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。
Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:张业成
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):论文推荐 | 解码城市街道景观骨架与城市活动之间的关联:利用大众点评数据在北京进行的实验
 规划问道
规划问道









