本期为大家推荐的内容为论文《Simulation of urban non-motorized traffic: A agent-based modeling approach based on big data of bike sharing and social force model》(城市非机动车交通仿真:基于自行车共享大数据和社会力模型的智能体建模方法),发表在Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology期刊,欢迎大家学习与交流。
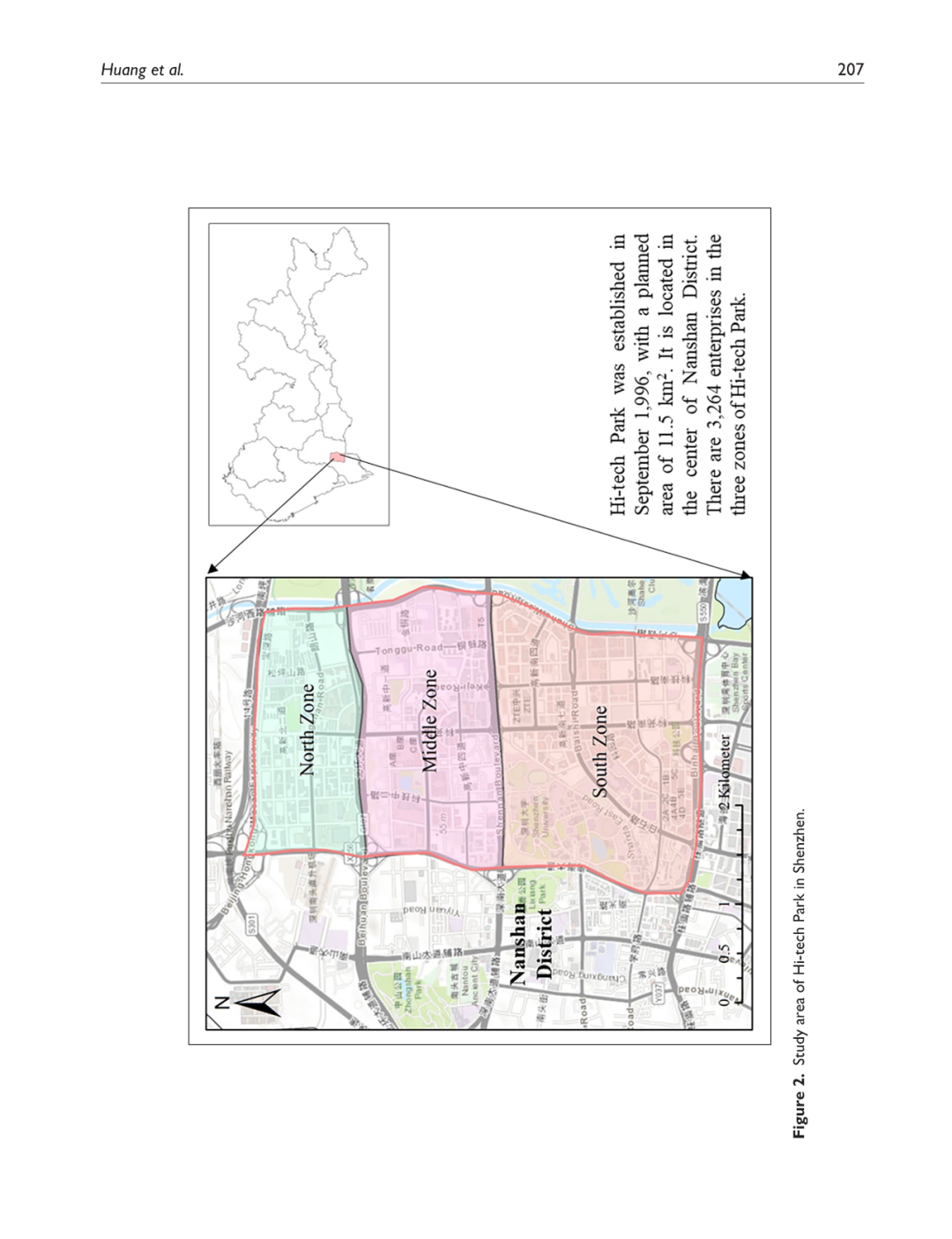
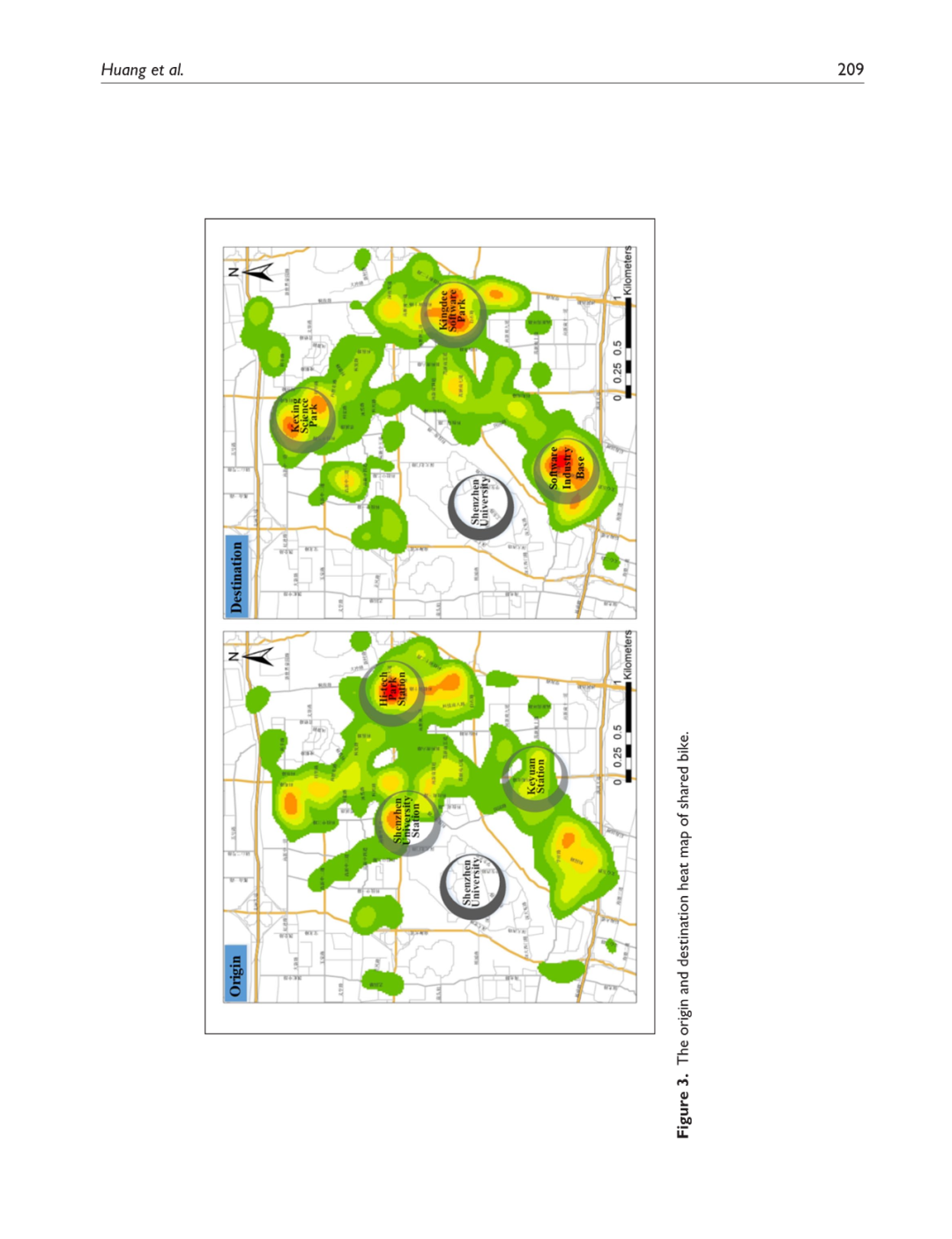
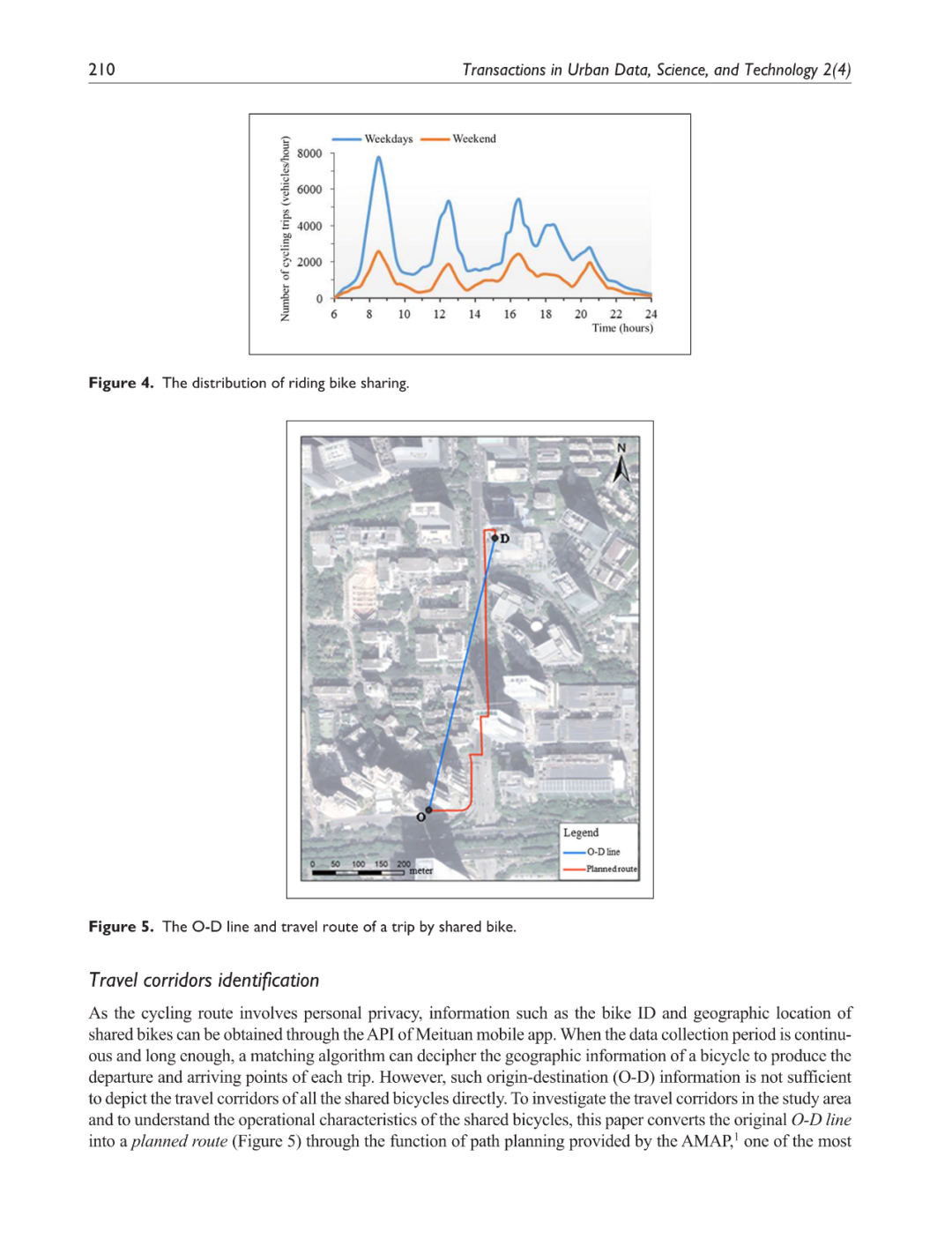
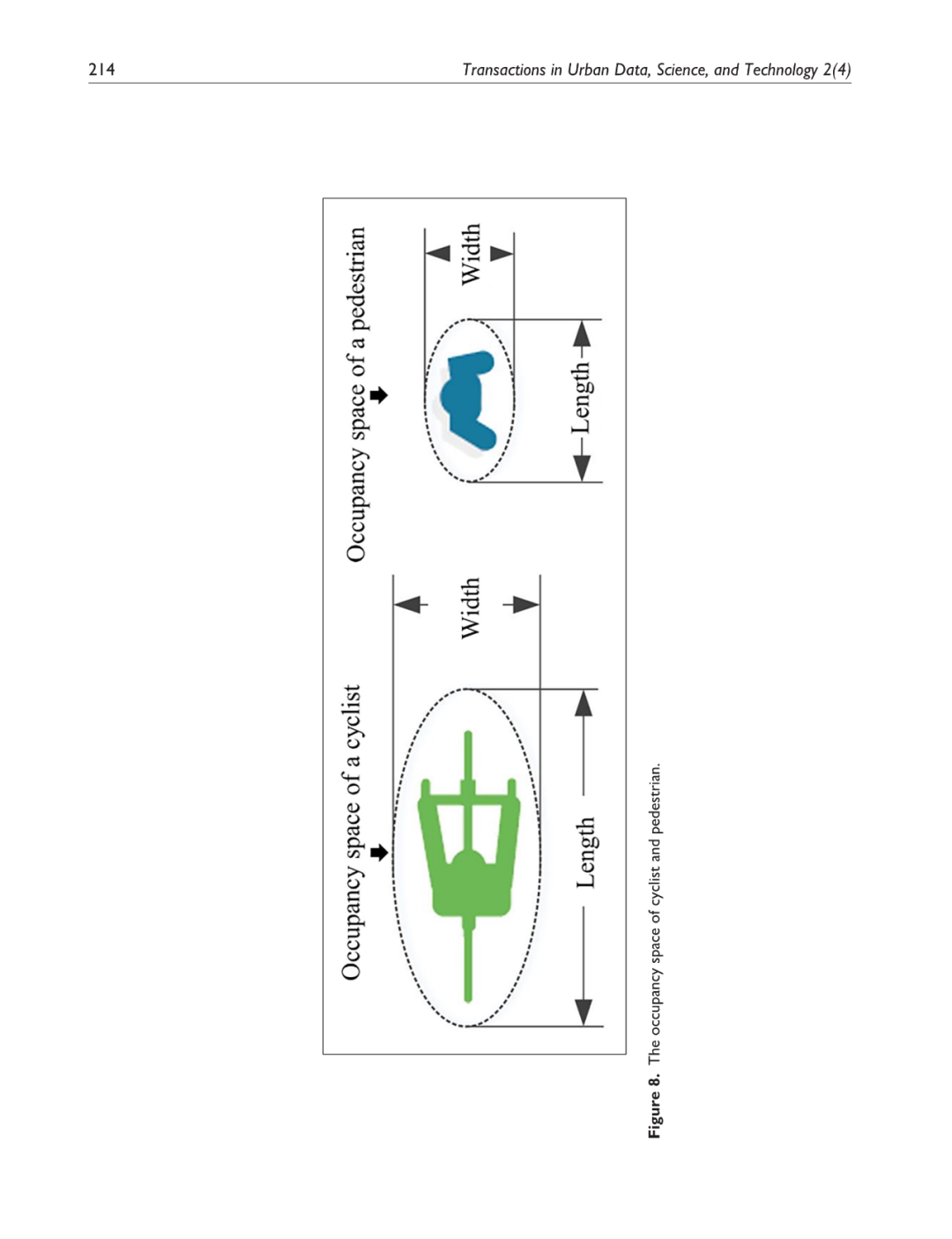
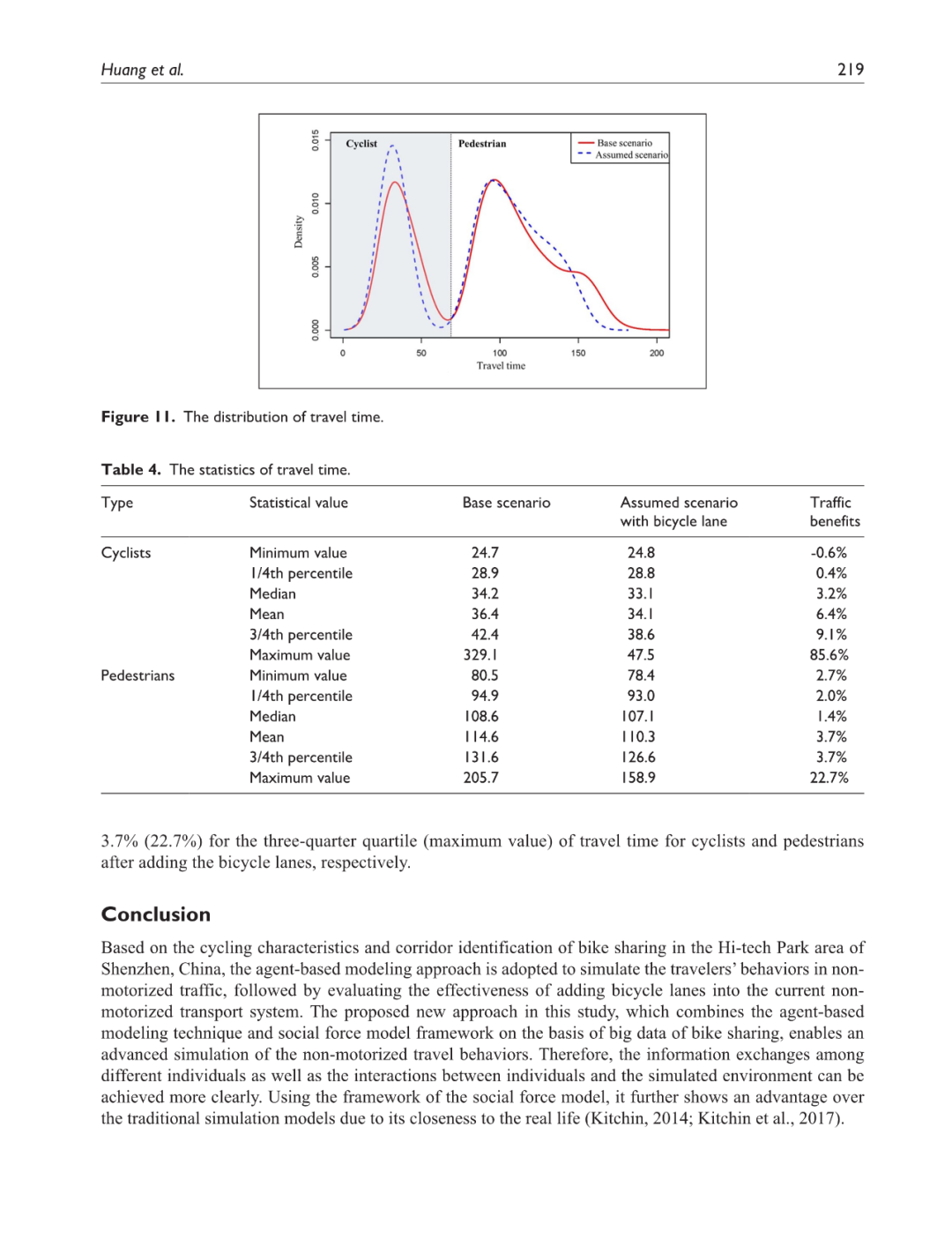
鼓励使用自行车这种城市非机动交通方式已被广泛认可为一种环境友好的方式,它可以缓解城市交通拥堵并解决“最后一公里”问题。然而,由于自行车道权利不明确和非机动车道不连续,城市规划者对城市骑行的效率和安全性普遍表示担忧。本研究利用深圳高科技园区美团自行车(前身为摩拜单车)的动态位置数据,分析共享自行车使用的时空变化,旨在识别自行车交通走廊。结合基于智能体的建模技术和社会力模型,本研究提出了一种新的模拟城市非机动交通的方法,因此为建设自行车走廊的自行车道提供了宝贵的洞见。结果显示:(1)工作日共享自行车的使用量是周末的2.5倍,骑行走廊通常是靠近地铁站的主要和次要道路;(2)增加自行车道可以将非机动车流量的交通密度整体降低6%,并分别节省自行车骑行者和行人的出行时间6.4%和3.7%。


题目:Simulation of urban non-motorized traffic: A agent-based modeling approach based on big data of bike sharing and social force model
(城市非机动车交通仿真:基于自行车共享大数据和社会力模型的智能体建模方法)
作者:
发表刊物:
Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1177/27541231231180989
引用格式:
Huang, W., Guo, Y., Guo, C., Tang, F., Zhao, Y., Xia, Z., & Zhang, R. (2023). Simulation of urban non-motorized traffic: A agent-based modeling approach based on big data of bike sharing and social force model. Transactions in Urban Data, Science, and Technology, 27541231231180989.
摘要ABSTRACT





更多内容,请点击微信下方菜单即可查询。
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。
Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:张业成
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):论文推荐 | 城市非机动车交通仿真:基于自行车共享大数据和社会力模型的智能体建模方法
 规划问道
规划问道









