本期为大家推荐的内容为论文《Different perspectives are indispensable for public space quality: Exploring the relationship between urban design quality and physical disorder》(不同的视角对于公共空间品质不可或缺:探讨城市设计质量与空间失序之间的关系),发表在 Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science 期刊,欢迎大家学习与交流。
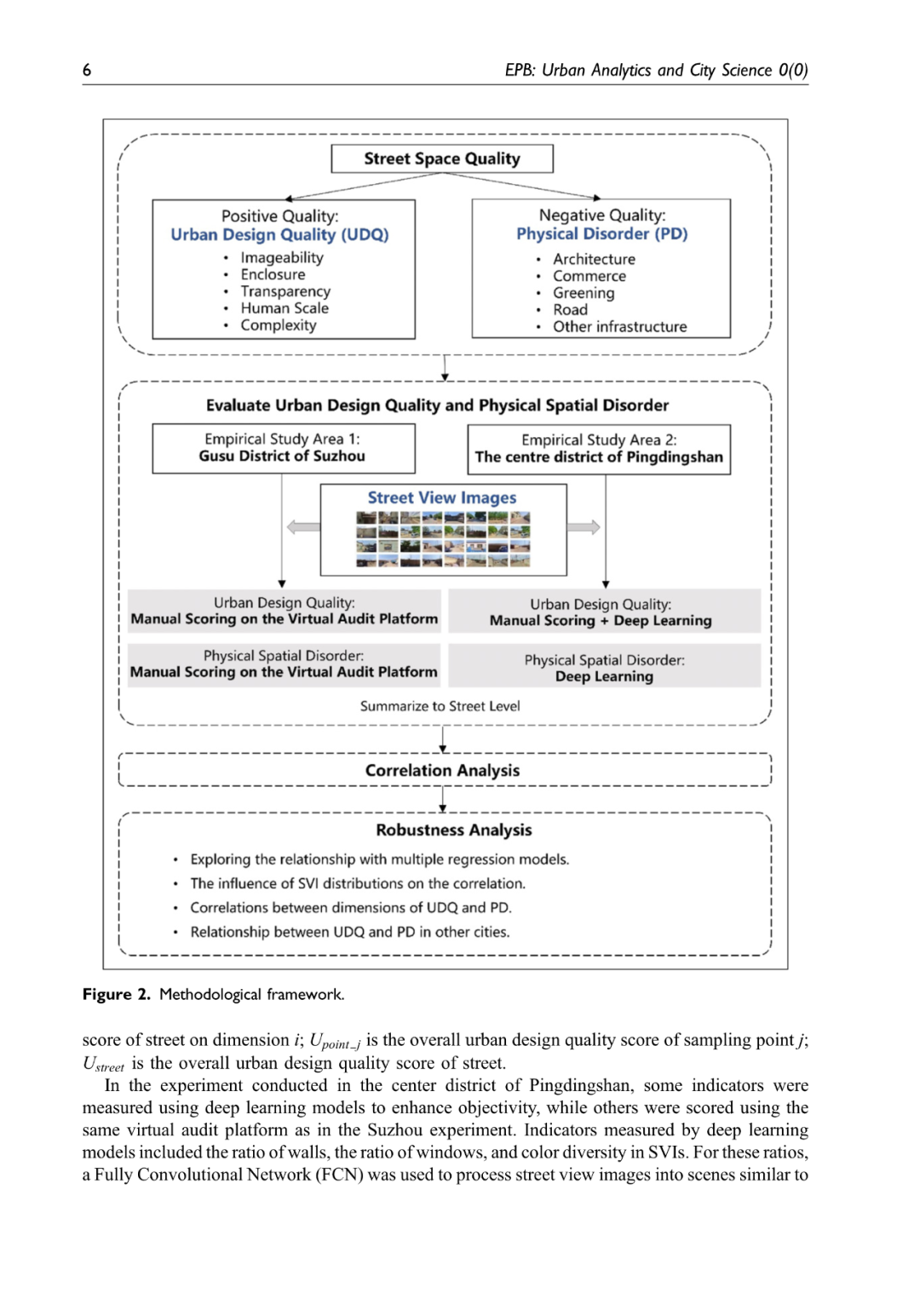
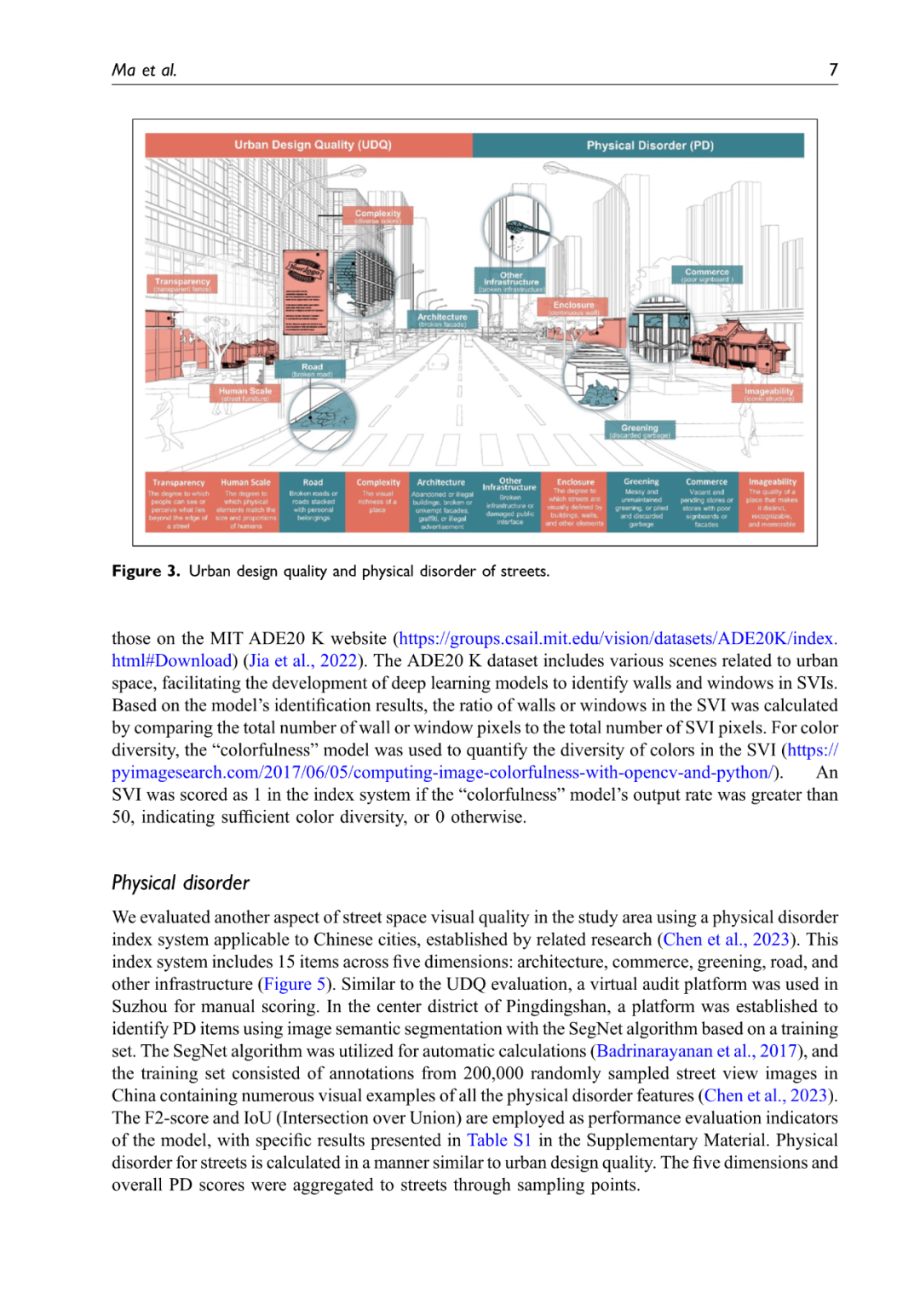
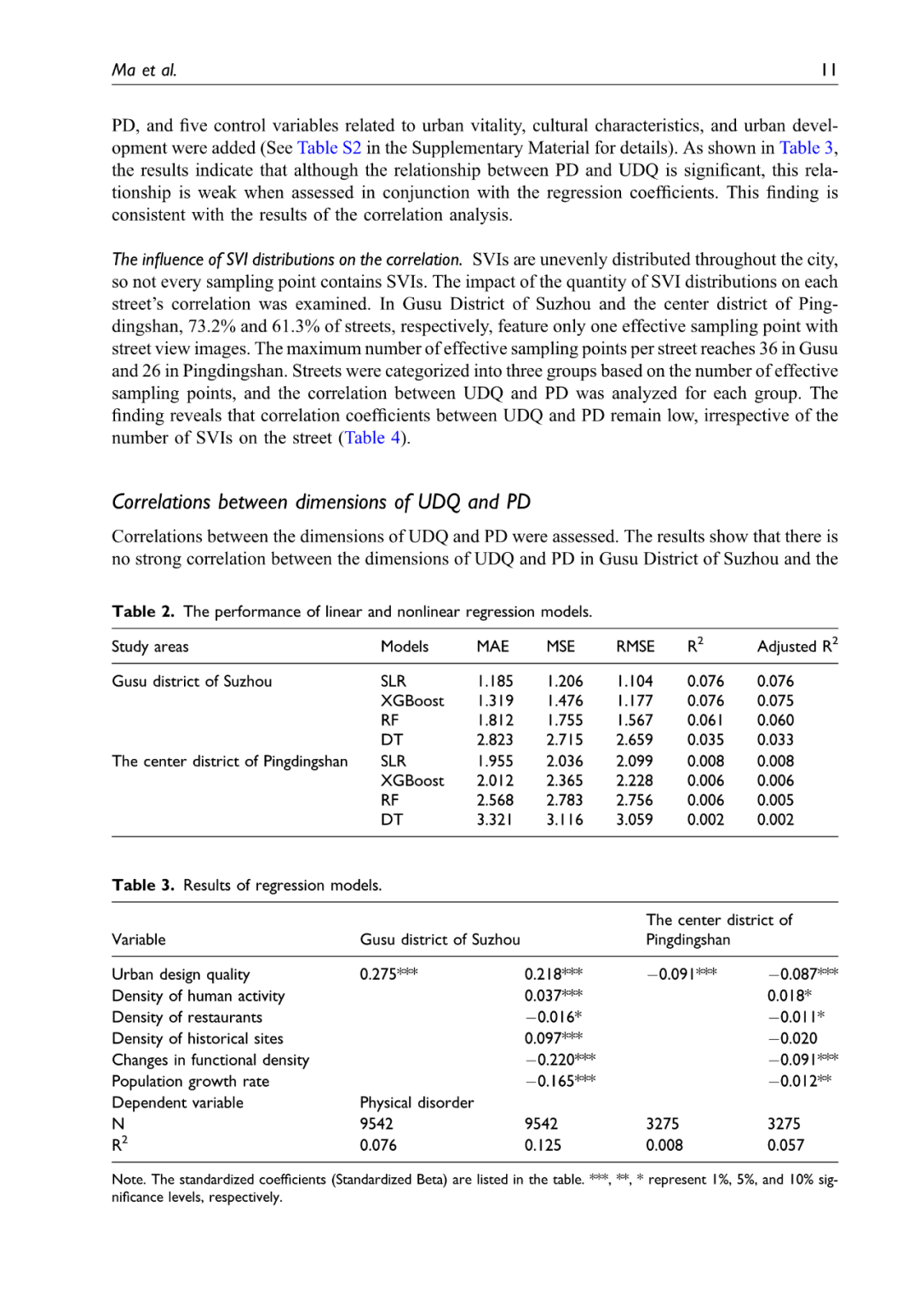
公共空间品质是一个多维概念,其中城市设计质量和空间失序分别从设计与维护的角度加以体现。然而,这两个因素之间的实际关系尚不明确,这也引发了关于是否有必要同时测量公共空间质量多个维度的问题。基于经典研究和理论,本研究分别构建了衡量这两项因素的指标体系,并利用人工虚拟审计和深度学习模型(包括 FCN 和 SegNet),结合大量街景图像,从城市设计质量和空间失序两个视角评估了中国两座城市的街道视觉质量,并探讨了二者之间的相关性。研究结果表明,在两座城市中,城市设计质量与空间失序的 Spearman 相关系数分别为 0.308 和 −0.085,表明二者之间的相关性较弱或不明确。此外,研究构建的线性和非线性回归模型的拟合度及解释力均较低,进一步表明无法通过其中一个变量有效预测或解释另一个变量。在稳健性测试中,本研究进一步引入了与城市活力、文化特征和城市发展相关的控制变量,同时考虑街景图像的分布影响,深入到更精细的维度,并扩展研究范围至更广阔的地区,验证了上述结论的稳定性。研究发现,街道的设计水平与维护水平不能相互替代或混为一谈,单独考察任一因素均无法全面反映公共空间品质。因此,从不同的视角分别评估和改善公共空间品质至关重要。这些研究结果拓展了我们对高视觉质量街道空间的理解,并为城市规划者和相关决策者在提升街道空间品质方面提供了重要参考。


题目:Different perspectives are indispensable for public space quality: Exploring the relationship between urban design quality and physical disorder
(不同的视角对于公共空间品质不可或缺:探讨城市设计质量与空间失序之间的关系)
作者:Yue Ma, Tangqi Tu, Ying Long*
发表刊物:Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1177/23998083251326772
摘要ABSTRACT
Public space quality is a multidimensional concept. Urban design quality and physical disorder represent it from the perspectives of design and maintenance, respectively. However, the practical relationship between these two factors remains unclear, raising questions about the necessity of measuring multiple dimensions of public space quality simultaneously. Based on classical studies and theories, this study developed index systems for both factors. Utilizing artificial virtual auditing and deep learning models, including FCN and SegNet, the street visual quality of two Chinese cities was assessed from the perspectives of urban design and physical disorder using extensive street view images. The correlation between these two factors was explored. The results showed that the Spearman correlation coefficients for urban design quality and physical disorder were 0.308 and −0.085 in the two cities, respectively, indicating weak or unclear correlations. Additionally, the fit and explanatory power of the linear and nonlinear regression models constructed were poor, further demonstrating that it is difficult to predict and explain one variable using the other. In the robustness test, the results were further validated by including control variables related to urban vitality, cultural characteristics, and urban development, considering the impact of the distribution of the street view images, drilling down to more granular dimensions and extending the scope of the study to a wider area. The levels of design and maintenance of streets cannot be conflated or substituted, and neither can independently represent the overall space quality alone. Both are indispensable, making it crucial to separately assess and address space quality issues from different perspectives. These results broaden our understanding of high-visual-quality street space and provide references for urban planners and stakeholders in improving street space quality.







更多内容,请点击微信下方菜单即可查询。
请搜索微信号“Beijingcitylab”关注。

Email:BeijingCityLab@gmail.com
Emaillist: BCL@freelist.org
新浪微博:北京城市实验室BCL
微信号:beijingcitylab
网址: http://www.beijingcitylab.com
责任编辑:马悦,张业成
原文始发于微信公众号(北京城市实验室BCL):论文推荐 | 不同的视角对于公共空间品质不可或缺:探讨城市设计质量与空间失序之间的关系
 规划问道
规划问道









